Gila Monster vs Beaded Lizard: Key Differences Between Venomous Cousins
When comparing the Gila Monster vs Beaded Lizard, we’re examining North America’s only two species of venomous lizards. While closely related, these fascinating reptiles exhibit distinct differences in size, habitat preference, and behavior. The Beaded Lizard (Heloderma horridum) typically reaches lengths of 22-36 inches (56-91 cm), making it notably larger than its cousin, the Gila Monster (Heloderma suspectum), which averages 16-20 inches (40-50 cm).
Both species belong to the family Helodermatidae and share similar venomous capabilities, but their geographic distributions rarely overlap. Gila Monsters inhabit the southwestern United States and northwestern Mexico, while Beaded Lizards range through Mexico’s western and southern regions into Guatemala.
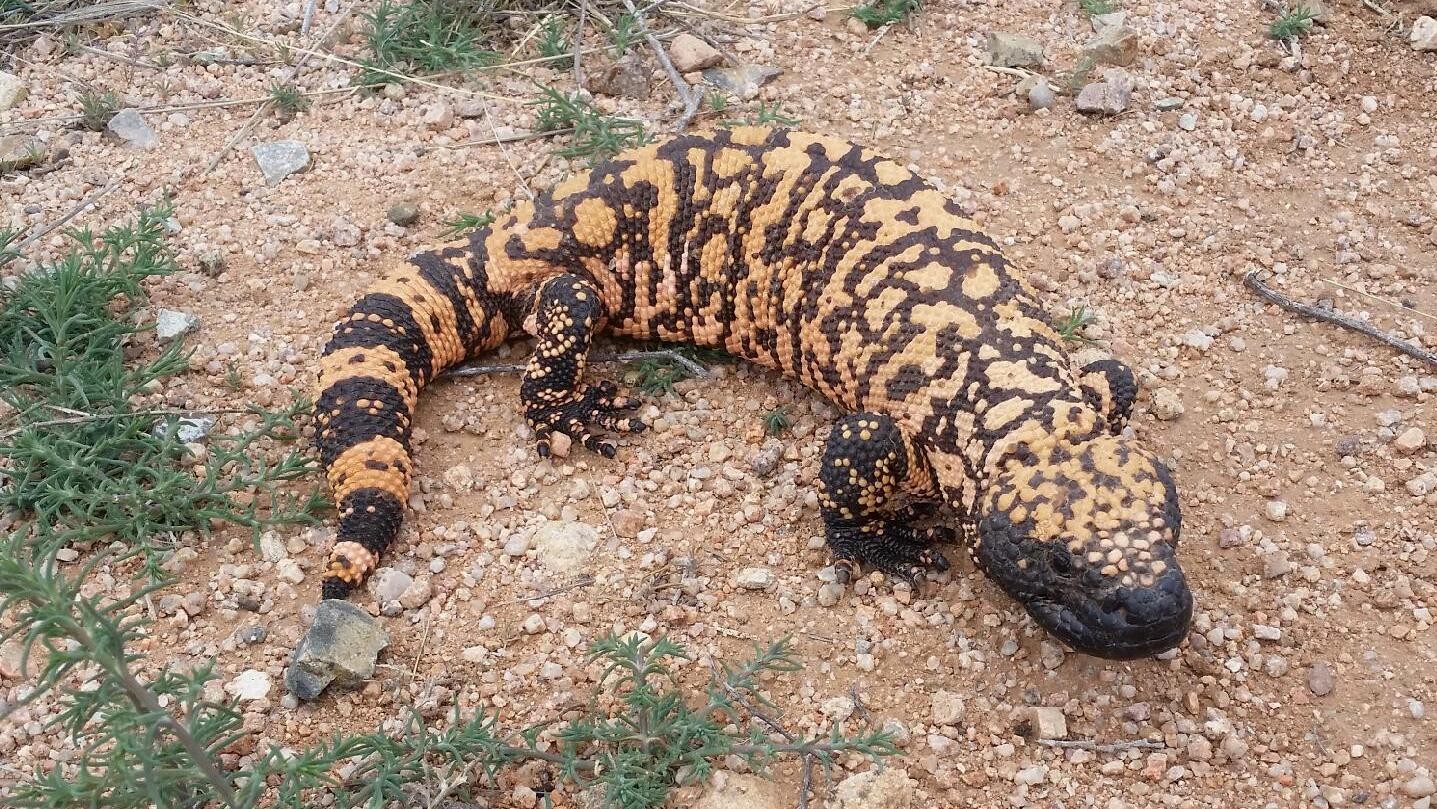

© Josh Olander / CC BY 4.0
The Gila Monster’s distinctive orange and black banded pattern serves as a warning signal to potential predators. These stocky lizards possess powerful jaws and venomous glands, making them formidable despite their relatively small size.
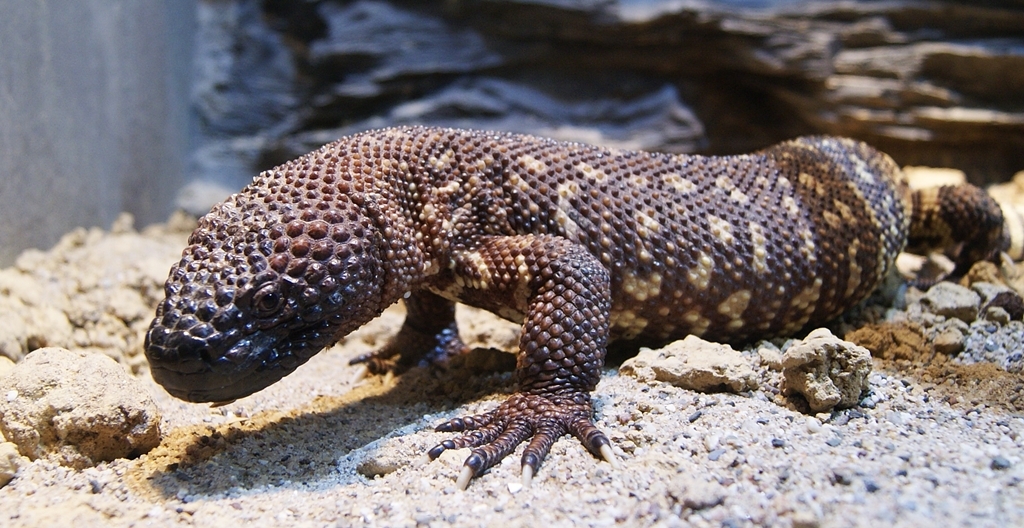

© Danny S. / CC BY-SA 4.0
The Beaded Lizard displays a more subdued coloration of black with yellow or brown mottling. Its larger size and more elongated body distinguish it from its northern relative, while maintaining the characteristic beaded scales that give both species their armored appearance.
Key Differences Between Gila Monsters and Beaded Lizards
| Feature | Gila Monster | Beaded Lizard |
|---|---|---|
| Size | 16-20 inches (40-50 cm) | 22-36 inches (56-91 cm) |
| Weight | 3-5 lbs (1.4-2.3 kg) | 4-8 lbs (1.8-3.6 kg) |
| Coloration | Orange/pink and black bands | Black with yellow/brown mottling |
| Habitat | Desert and semi-desert | Tropical dry forest |
| Range | Southwestern US, NW Mexico | Western/Southern Mexico, Guatemala |
| Activity Period | Primarily spring and early summer | Active year-round |
Habitat and Distribution
Gila Monsters thrive in arid desert environments, spending up to 95% of their time underground in burrows. They emerge primarily during the spring and early summer months to feed and mate. In contrast, Beaded Lizards inhabit tropical dry forests and thornscrub habitats, where they maintain more regular surface activity patterns throughout the year.
Venom and Hunting Behavior
While both species are venomous, their hunting strategies differ slightly. Gila Monsters rely heavily on their acute sense of smell to locate prey, primarily targeting eggs and young birds in ground nests. Beaded Lizards maintain a broader diet, including small mammals, birds, eggs, and other reptiles.
Conservation Status and Human Interaction
Both species face similar conservation challenges:
- Habitat loss due to urban development
- Collection for the illegal pet trade
- Human persecution due to fear
- Road mortality
The Gila Monster is protected throughout its range in the United States, while the Beaded Lizard is considered vulnerable in many parts of its range.
Who Would Win in a Fight?
While such encounters wouldn’t occur naturally due to separate ranges, a theoretical match-up between these venomous lizards would likely favor the Beaded Lizard due to its:
- Larger size and mass
- More powerful bite force
- Greater overall strength
- Longer reach
However, both species are typically non-aggressive and avoid confrontation when possible, preferring to focus their energy on finding food and maintaining territory.
Frequently Asked Questions
Which is more venomous: Gila Monster or Beaded Lizard?
Both species possess similar venom potency, but the Gila Monster typically delivers a more persistent bite. Neither species has caused a confirmed human fatality in recorded history.
Can Gila Monsters and Beaded Lizards be kept as pets?
While both species are protected by law, some states allow permitted facilities and licensed individuals to keep them. However, they require specialized care and are not suitable as typical pets.
How long do these lizards live?
In captivity, both species can live 20-30 years, with Gila Monsters typically living slightly longer than Beaded Lizards under optimal conditions.